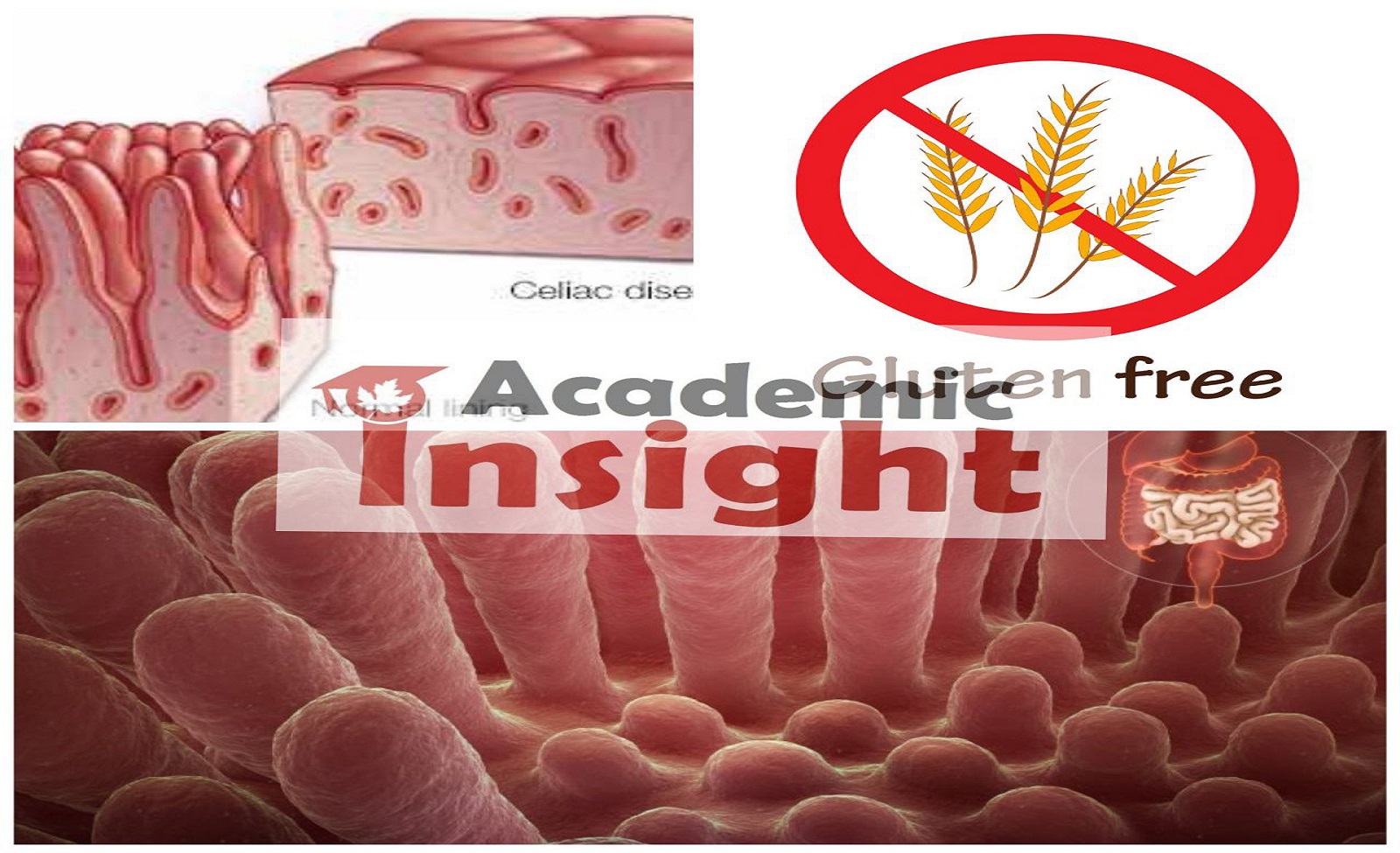
Celiac disease is an immune system response to eating gluten, a protein found in barley, rye, and wheat.
If you have celiac disease,. After some time, this reaction damages your small intestine’s lining and prevents it from absorbing some nutrients (malabsorption). The intestinal damage often leads to weight loss, fatigue, diarrhea, bloating and anemia, and can lead to serious complications.
In children, malabsorption can affect growth and development, besides causing the symptoms to appear in adults.
There’s no treatment for celiac disease — however for most people, following a completely gluten-free diet can help manage symptoms and promote intestinal healing.
Symptoms of celiac disease
The symptoms of celiac disease can differ and vary completely in children and adults. Some digestive symptoms for adults involve:
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Constipation
- Weight loss
- Gas and bloating
- Vomiting and nausea
But, more than 50% of the adults with celiac disease have some signs and symptoms unrelated to the digestive system, like:
- Anemia, typically from iron deficiency
- bone density Loss (osteoporosis) or softening of bone (osteomalacia)
- blistery, Itchy skin rash
- Mouth sores
- Fatigue and headaches
- Nervous system injury, including tingling and numbness in the feet and hands, probable difficulties with cognitive impairment, and balance
- Joint pain
- spleen function Reduction
What are common symptoms in children?
Children with celiac disease are more probable than adults to have digestive problems, involving:
- Vomiting and nausea
- Constipation
- Chronic diarrhea
- Swollen belly
- Gas
- Pale, foul-smelling stools
The failure to absorb nutrients can lead to:
- Tooth enamel Destruction
- Failure to thrive
- Weight loss
- Anemia
- Short height
- Irritability
- Delay in puberty
- Neurological symptoms, including attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (better known as ADHD), headaches, learning disabilities, seizures, and lack of muscle coordination.
Dermatitis herpetiformis
Gluten intolerance may cause this blistering, itchy skin disorder. The rash typically happens on the elbows, scalp, torso, knees and buttocks. This condition is often associated with some changes to the lining of the small intestine identical to those of celiac disease, but the skin condition usually doesn’t lead to digestive symptoms.
Medical practitioners treat dermatitis herpetiformis with medication or a gluten-free diet, or both, to control the rash.
disclaimer
Don’t forget that you should always seek the guidance of your practitioner or other qualified health professional with any questions you might have regarding your health or a medical condition. Never forget about the advice of a medical professional, or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this or any other Website.